Why The Auto Reports Lab?
TheAutoReportsLab takes the mystery out of the history
Fast, no-hassle turn
around
TheAutoReportsLab gives you the best value for your money
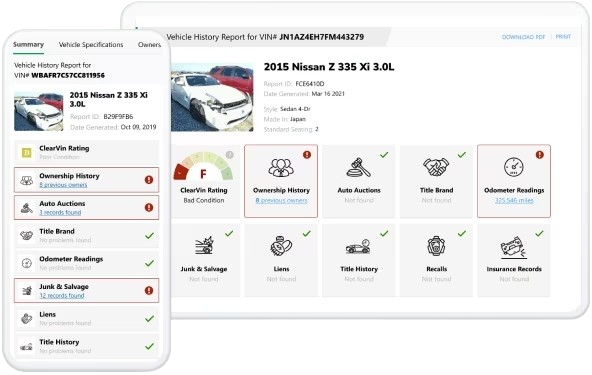
Free VIN Check Report Sample
How to Decode a VIN?
Though it is easy to locate a VIN, decoding the information contained in every VIN might be a challenge. The 17 digits of the VIN are divided into segments and each represents some relevant information about the vehicle including the year, make and model, country, and factory of manufacture, serial number, etc.
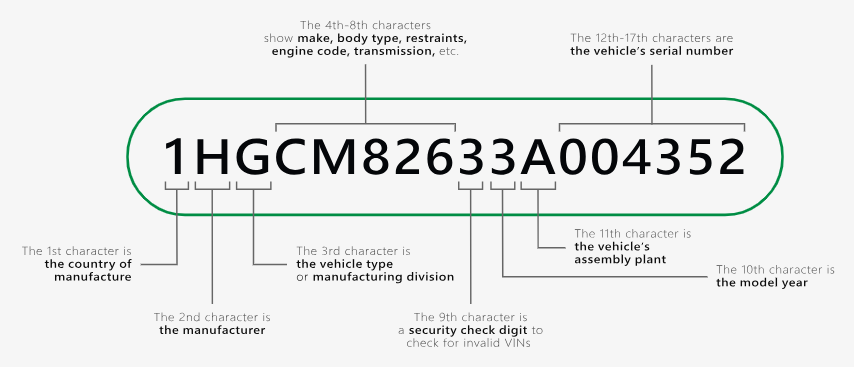
The first three characters of a VIN, known as the World Manufacturer Identifier (WMI), indicate the manufacturer and the country of origin, helping to identify the vehicle’s make and model. Each manufacturer has one or more assigned WMI codes, which are regulated by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) under the oversight of the International Organization for Standardization.
The following six characters, often called the Vehicle Descriptor Section (VDS), provide details about various features, including the vehicle’s body type, engine size, and transmission type. In the U.S., it’s required to include information on gross vehicle weight and installed safety systems. The 9th character is the check digit, used to verify the authenticity of the VIN, and can be a digit from 0 to 9 or the letter “X.”
The final part, the Vehicle Identifier Section (VIS), completes the VIN. The 10th character typically indicates the model year or production year, while the 11th character reveals the assembly plant. The remaining numeric characters represent the vehicle’s serial number. At 1 DigitalCheck, our VIN number decoder automatically retrieves vehicle information by VIN code and presents it in an easy-to-read format.
